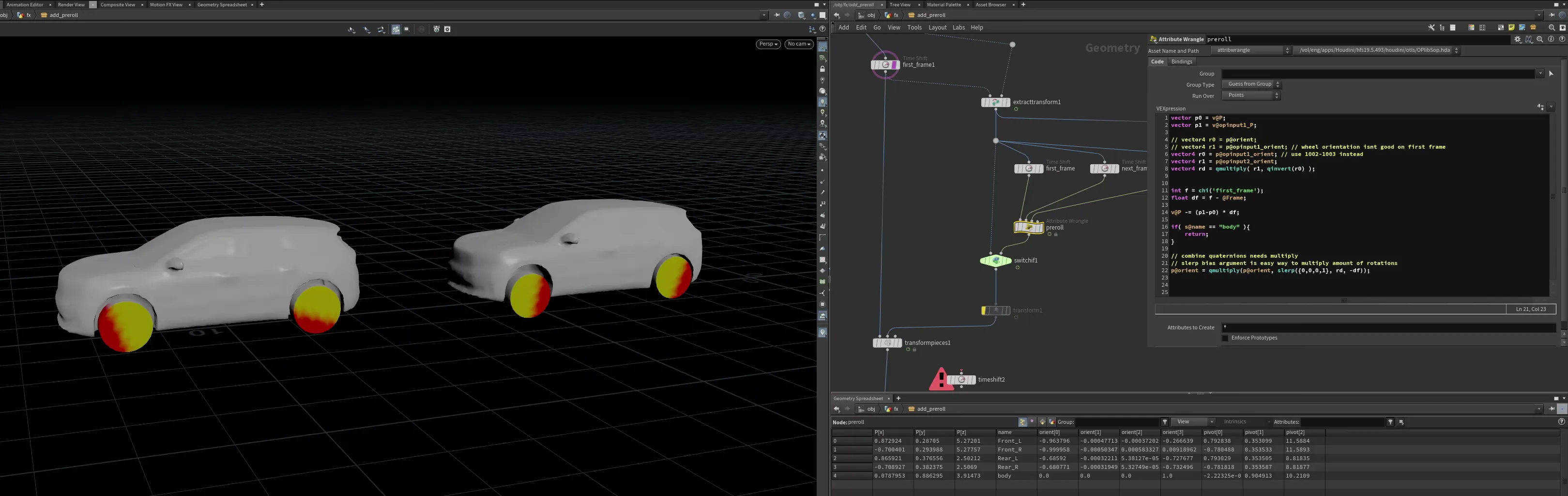
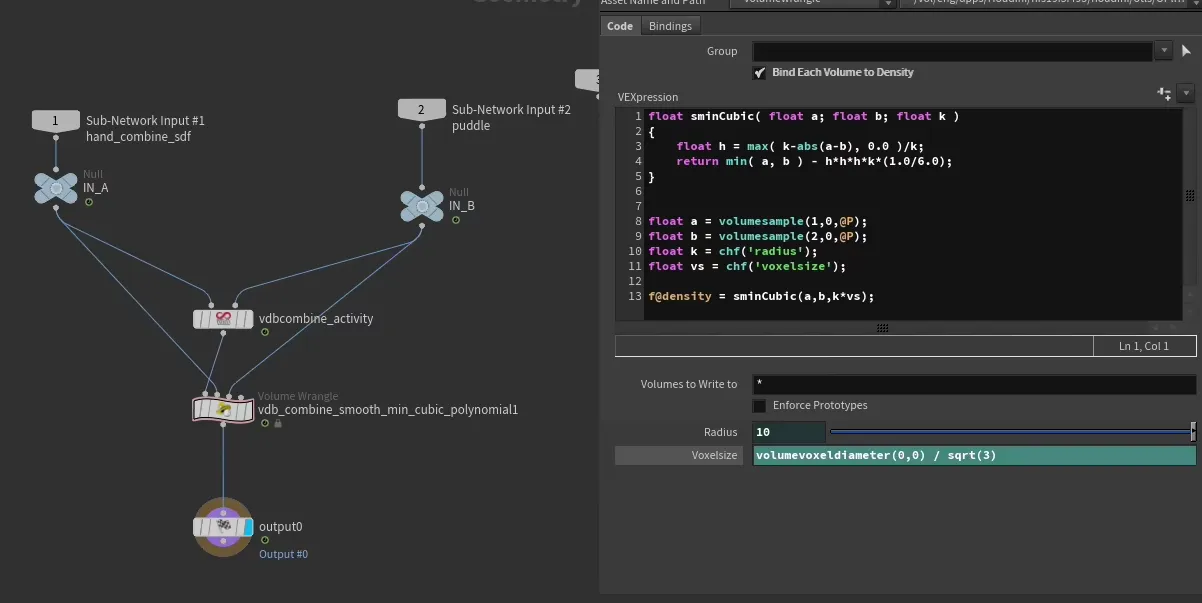
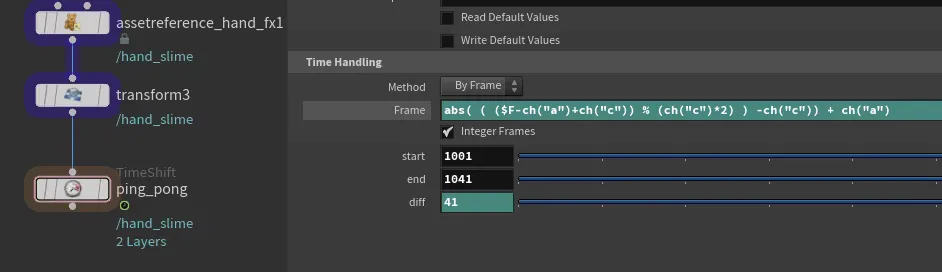
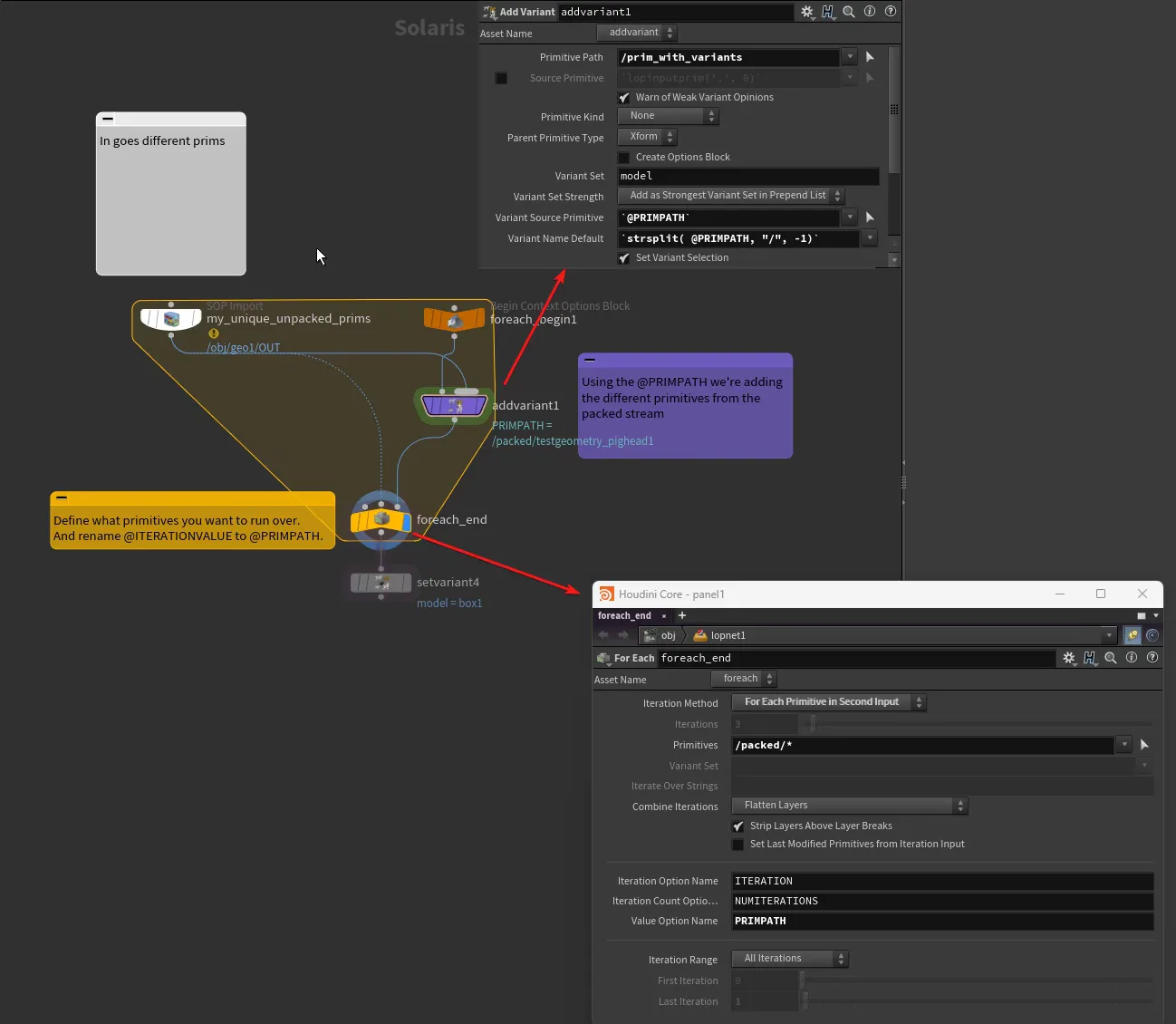
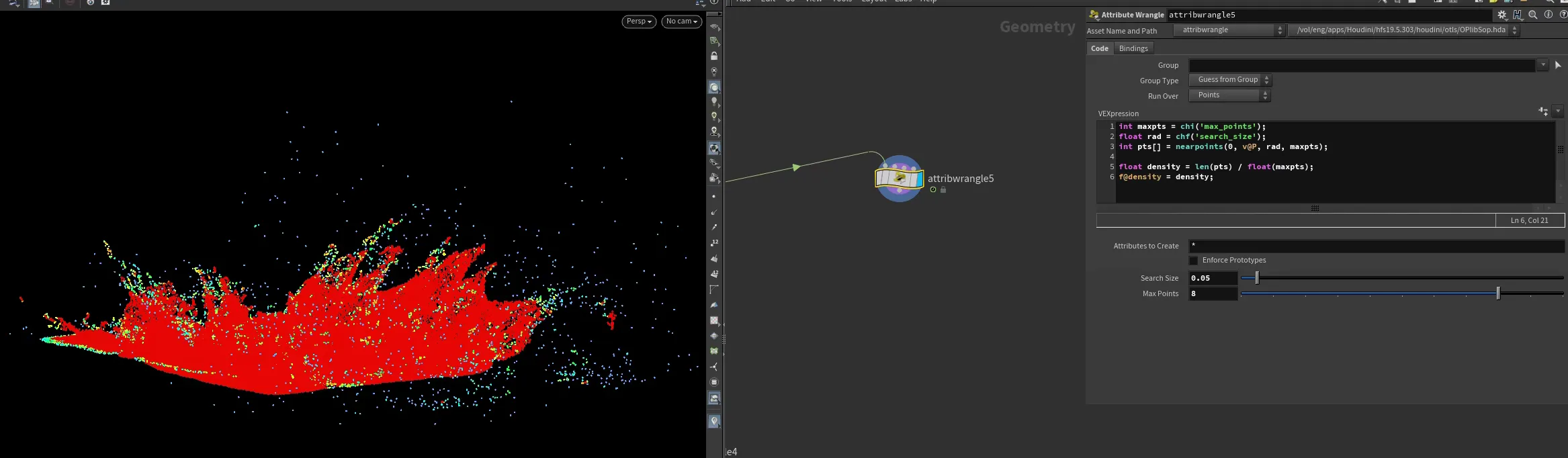
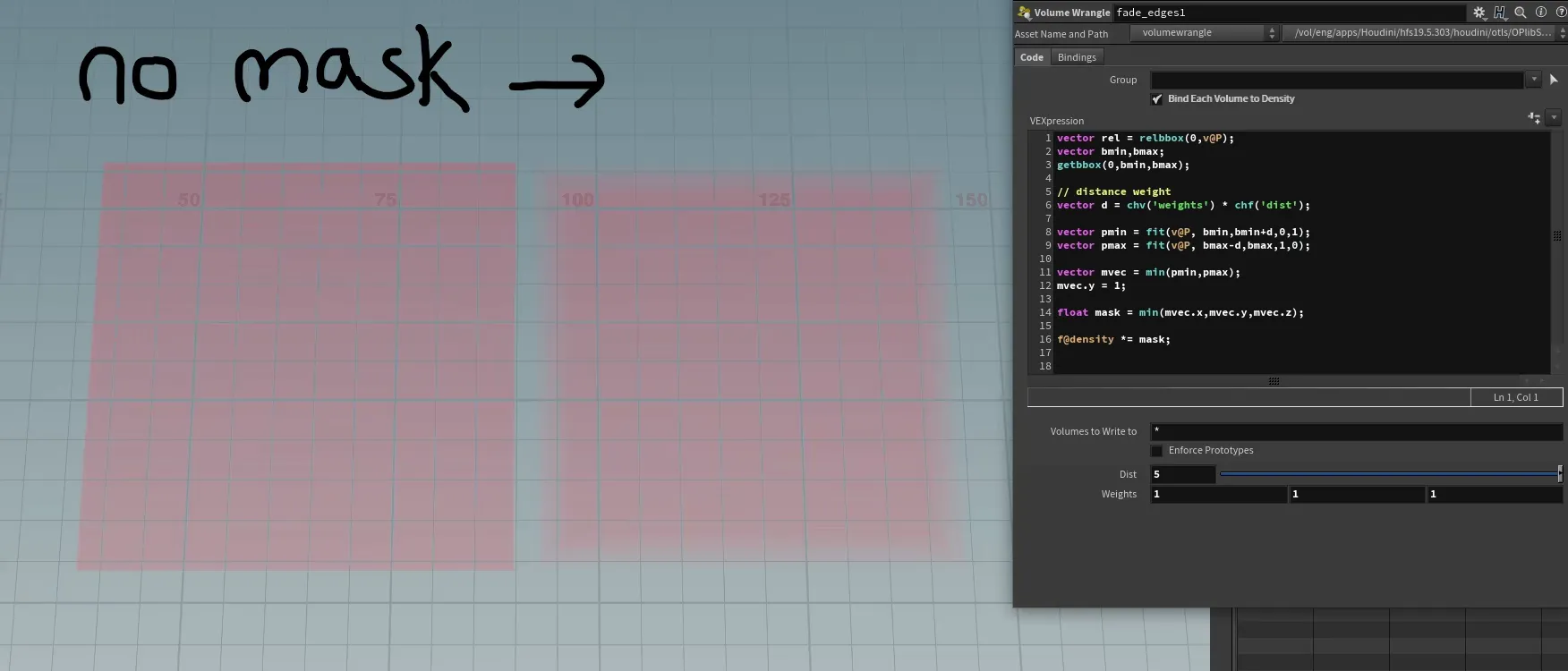
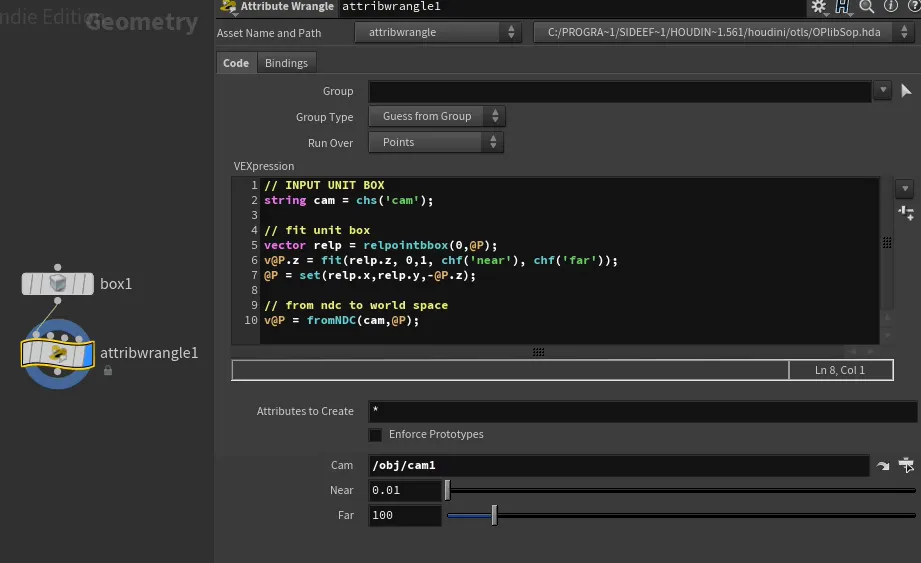
Bubbles in flip
https://www.nicholas-taylor.com/blog/bubble-trouble good general overview of bubble issues and solutions, especially flip reseeding (I prefer bruteforce large ptcount and avoid reseeding if possible)
// stop bubble pscale from overlapping
int numpts = chi('max_pts'); // neighbours to query
int pts[] = pcfind_radius(0, "P", "pscale", 2, @P, @pscale, numpts);
float sc = @pscale;
if(len(pts) > 1){ // only continue if overlapping point is found
int l = len(pts);
for(int i = 0; i < l; i++){
int pt = pts[i];
if(@ptnum != pt){ // ignore self
float pss = point(0, "pscale", pt);
vector ppos = point(0, "P", pt);
float d = distance(@P, ppos); // distance between centers
float a = (@pscale + pss)/2; // total combined radius
if(d < a){
float r = d / a; // ratio of radius sum to distance between centers
sc = min(sc, r*@pscale); // we want to use the smallest radius required
}
}
}
}
@pscale = sc;// ensure bubble pscale doesnt poke through surface
int hpr;
vector huv;
float dist = xyzdist(1, v@P, hpr, huv);
f@pscale = max(0,min(dist-0.001,f@pscale));